Atrial fibrillation (Afib, AF) is the most commonly diagnosed abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) in the U.S.: 1
- 8 million people in the U.S. have Afib1
- 2 million people in the U.S. are diagnosed with Afib each year1
- 1 in 4 adults will develop Afib in their lifetime2
- 33 million people around the world have Afib3
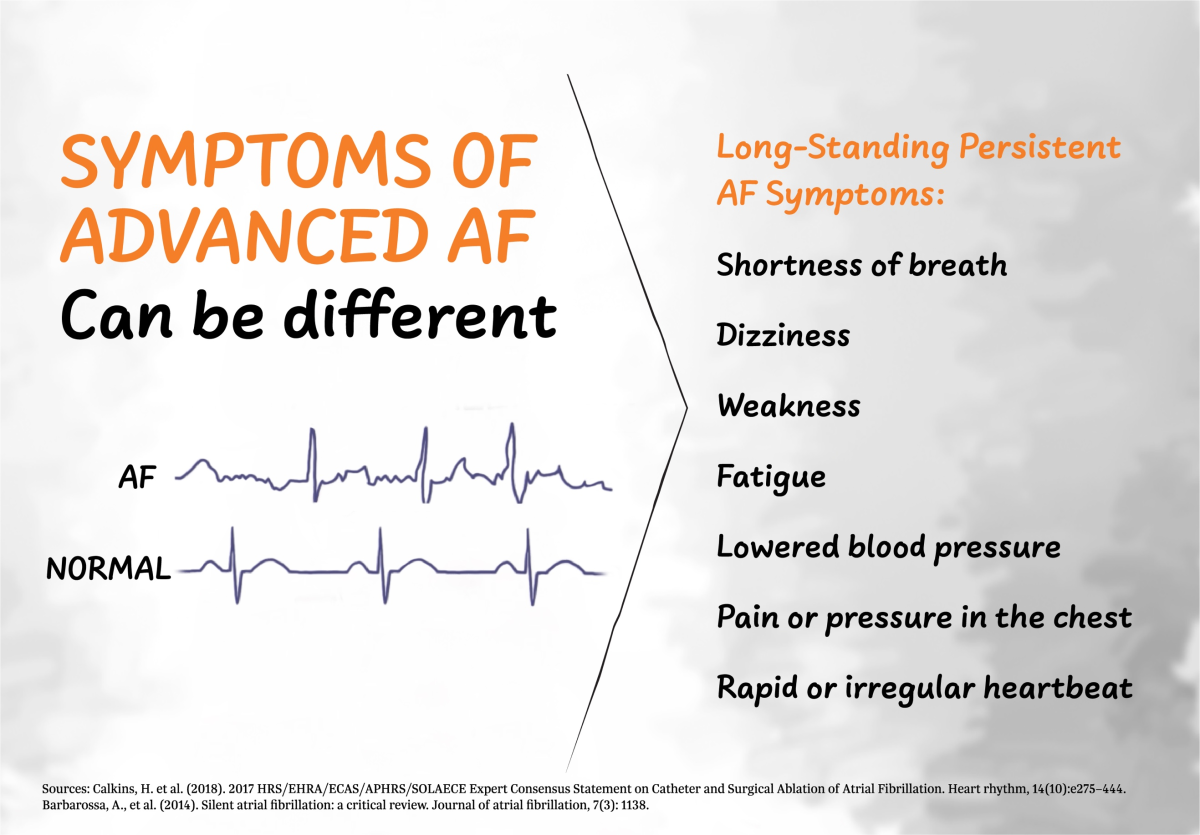
Atrial fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm caused by erratic electrical signals in the heart. A normal heart rhythm creates regular electrical signals that travel through the heart. The signals are essential for the heart to beat in a steady, rhythmic way. This allows blood to be pumped to all parts of the body. Sometimes the electrical signals become irregular, and the heart beats abnormally.
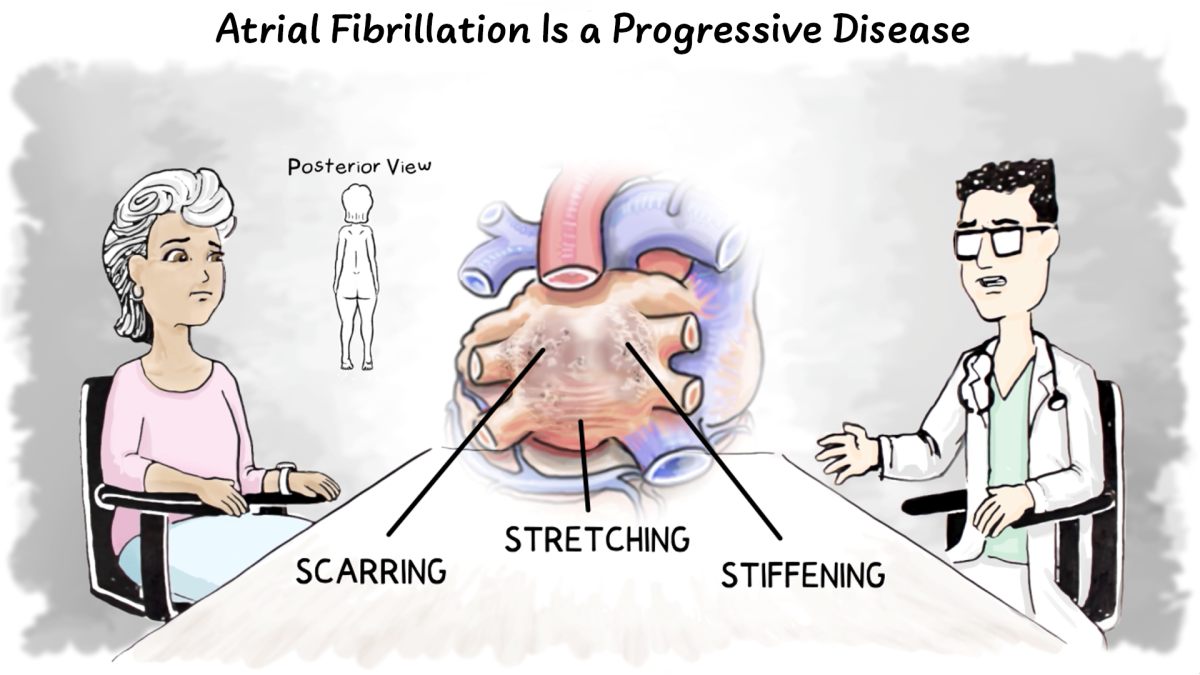
Atrial fibrillation is also called Afib or AF. If not properly treated, it can grow worse over time and possibly damage your heart. Atrial fibrillation can also lead to health problems:
5x increase in stroke risk4
5x increase in heart failure development5
Atrial fibrillation also leads to a higher risk of:6
- Chronic fatigue
- Decreased activity level
- Decline in quality of life
It’s best to have atrial fibrillation treated before it progresses and causes other health problems.7
Even after people develop other heart problems, there is hope. When atrial fibrillation is successfully treated it can:
- Reverse the stretching of the left atrium7
- Improve heart function overall7
- Improve your symptoms8
- Reduce the number of heart medications you need7